Preschool Years
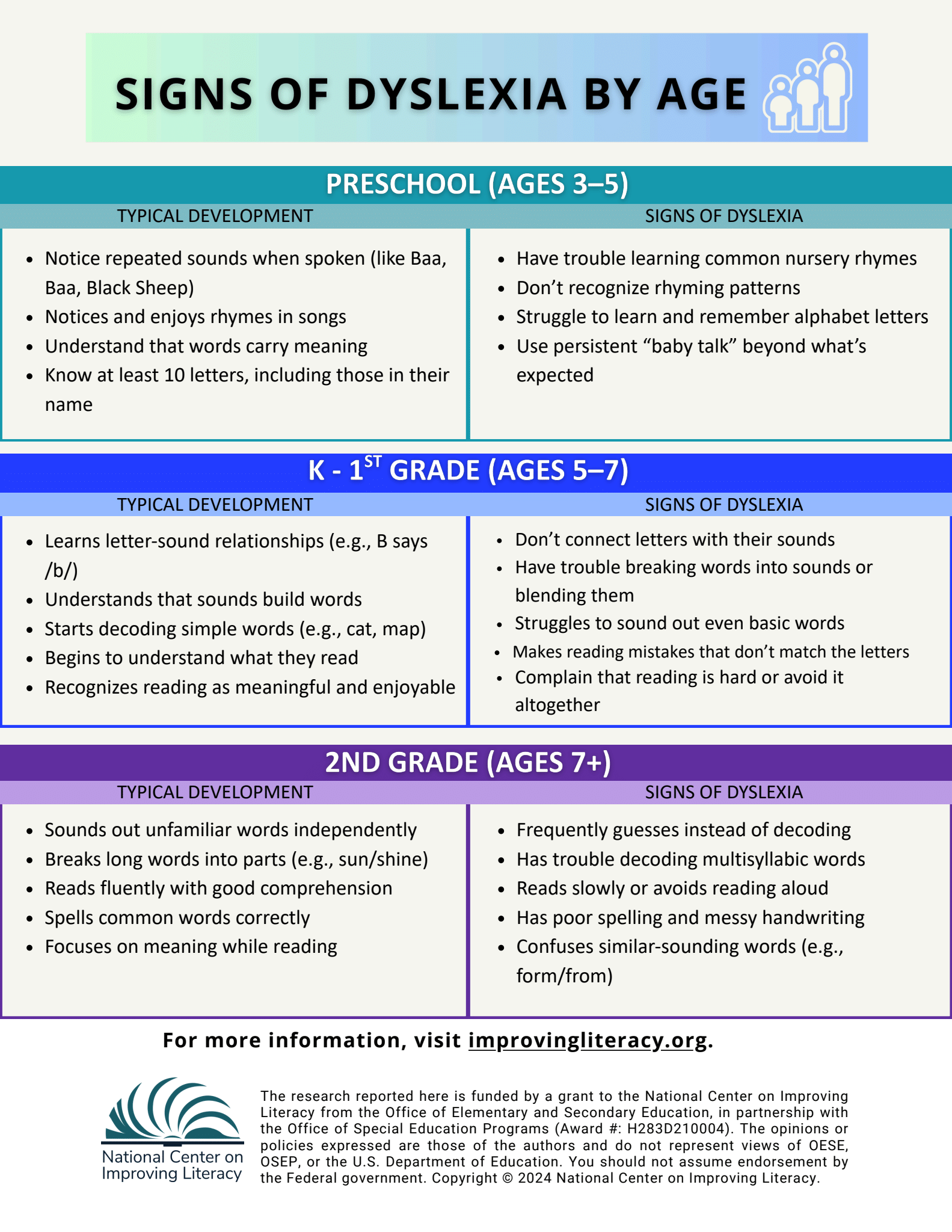
Age: 3-5
In the preschool years, many children begin developing an awareness of sounds in language and the concept of print. Typical readers at this age often:
-
Enjoy playing with sounds and rhymes
-
Recognize some letters, especially those in their name
-
Begin to understand that printed words carry meaning
Children at risk for dyslexia, on the other hand, may:
-
Struggle to learn common nursery rhymes
-
Not recognize rhyming patterns
-
Have trouble remembering letter names
-
Continue to use “baby talk” well past toddlerhood
These early difficulties can point to challenges with phonological awareness—an early warning sign of reading difficulties
Kindergarten to 1st Grade
Age: 5-7
As children move into kindergarten and first grade, they typically learn how letters map to sounds and begin to read simple words. Most readers at this stage:
-
Understand letter-sound relationships
-
Can decode regular one-syllable words like cat, map, or pan
-
Begin to comprehend what they read
Children at risk for dyslexia may show a different pattern. They might:
-
Not connect letters with sounds
-
Make reading mistakes that don’t match the letters on the page
-
Struggle to break words into sounds
-
Avoid reading or express frustration
These challenges often suggest difficulties in phonics and decoding—core components of early reading.
2nd Grade and Beyond
Age: 7+
By second grade and up, most children begin to read more fluently and focus on understanding longer texts. Typically developing readers:
-
Use letter-sound knowledge to read unfamiliar words
-
Decode longer, multisyllabic words using word parts
-
Read with enough fluency to focus on comprehension
Children at risk for dyslexia may:
-
Continue to struggle with decoding
-
Read slowly or guess at words
-
Confuse similar-sounding words
-
Avoid reading aloud
-
Show persistent difficulties with spelling and handwriting
At this stage, reading difficulties become more pronounced and can affect a child’s confidence and academic performance if not addressed.